Mobile communications requires close interworking between a mobile device such as a mobile phone and a mobile network which in turn connects to the telephone network and the internet. The mobile phone or other mobile device represents some of the toughest design challenges in the mobile chain. The phone has to be small light rugged have good battery life as well as being smart and easy to use.
Originally it was enough that a mobile could make and receive voice calls now this requirement is one of literally dozens of capabilities required. You can see examples of mobiles used in Australia starting in 1987 in the History
tab on this site here.
While the early PAMTS and AMPS phones were assembled in Australia by NEC and Mitsubishi respectively, as with AM radio and TV sets, subsequently almost all devices were made offshore. In the analogue mobile era Motorola dominated with around 60% world market share. The full story of Motorola’s climb and fall from fame in this space is HERE.
In the 2G digital era Nokia came to dominate the market only to be unseated and subsequently sold to Microsoft who closed the brand in 2014. In 2007 Nokia enjoyed a 50% world market share of mobile phone sales. Seven years later it was out of the market as a brand. Nokia’s demise came as a result of it missing the move to smartphones where its Symbian operating system was totally uncompetitive with Apple’s iOS and subsequently Google’s Android. Nokia’s rise and fall from fame is covered HERE.
Currently smartphones represent around 80% of cellular network connections worldwide. The other 20% are connected PC, tablets, mobile WiFi dongles and feature phones. Feature phones are not sold at all in the developed world including Australia so smartphones are the dominant mobile device type
Smart Phones
In the smartphone era the two operating systems iOS and Android have come to dominate the market. Presently Apple which is the only supplier of iOS devices has around 17% of the world market but enjoys much stronger support in Australia, North America, Japan and UK. Android which was acquired by Google in July 2005 is licensed to almost all other phone manufacturers. A history of how the Android OS came to dominate the world of mobiles is HERE.
The Canalys graphs below show the world smart phone vendor share and total sales.
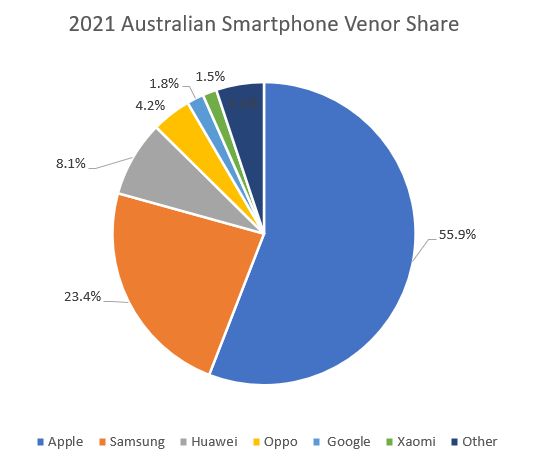
The smartphone share by vendor for Australia is shown on the chart below.
A few examples of top smartphones today will serve to illustrate just how far mobile phone development has come.
Samsung Galaxy S22
 The Galaxy S22 in its various guises is market leader Samsung’s premium smartphone. As with most mobile device manufacturers the Galaxy S22 is in a line of annual updates which have seen new features and improvements. It comes with Android 12 with Samsung’s Android custom interface One UI. It has a 6.1 inch 1080X2340 20:9 aspect HDR10+, 120Hz refresh, 1300 nit AMOLED screen and a 3.7 AH battery which can fully charge at up to 25W in around 50 minutes.
The Galaxy S22 in its various guises is market leader Samsung’s premium smartphone. As with most mobile device manufacturers the Galaxy S22 is in a line of annual updates which have seen new features and improvements. It comes with Android 12 with Samsung’s Android custom interface One UI. It has a 6.1 inch 1080X2340 20:9 aspect HDR10+, 120Hz refresh, 1300 nit AMOLED screen and a 3.7 AH battery which can fully charge at up to 25W in around 50 minutes.
It has three front facing cameras a 12 and a 50 M pixel and a 10MP 3X zoom camera plus 10 MP selfie camera. It can shoot video to 8K 24 fps. It comes with 8 GB LPDDR5 RAM and either a 128 or 256 GB flash drive.
As with all Android phones it is designed around a system on chip SoC which provides the data and communications processing. Samsung makes a range of these SoCs which they use on the majority of their phones. The top of the line of these is the 4nm Exynos 2200 which is fitted to S22s for Europe however Samsung fits Qualcomm’s top spec device Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 to phones for the rest of the World.
The Galaxy S22 is capable of:
- Voice Calls via 3G and VoLTE
- SMS
- MMS
- IM
- RSS
- HTML5 Browser
- Packet Data on GSM/GPRS/EDGE, WCDMA/HSPA/HSPA+ to 42Mbps and 4G LTE 5G NR NSA SA including mmWave
- WiFi 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax to 3.6 Gbps
- A-GPS, GLONASS, BDS, GALILEO for Mapping and Location Based Services
- Near Field Communications NFC
- Bluetooth V5.3
- USB C (USB 3.1)
- Measurement using accelerometer, gyro, proximity, compass, barometer, temperature, humidity and gesture sensors under screen finger print sensor
The full specifications for the phone are on the GSM Arena web site Here.
 Galaxy S22 runs Android 12 and adds to Play Stores’ available 2.8 million apps:
Galaxy S22 runs Android 12 and adds to Play Stores’ available 2.8 million apps:
- Bixby voice assistant
- Active noise cancellation
- TV-out (via MHL 2 A/V link)
- Video playback Dolby Vision, HDR10+, HDR10, HLG, H.264 (AVC), H.265 (HEVC), VP8, VP9
- Audio player MP3/WAV/eAAC+/AC3/FLAC
- Organizer
- Image/video editor
- Document viewer (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, PDF)
- Google Search, Maps, Gmail, YouTube, Calendar, Google Talk, Picasa
- Voice memo/dial/commands
- Predictive text input
You can get an idea of the complexity in a small package by looking at a Teardown of the Galaxy S22. There is a Wiki covering the Galaxy S22 here .
Apple iPhone 13
 There were capable smart phones before but it is said that the iPhone kicked off the smart phone revolution when it launched in 2007. The original iPhone was not sold in Australia however the Australian launch in July 2008 of the iPhone 3G created huge interest. It has been followed by yearly upgrades. Apple have built a strong loyal following for their premium product and the iTunes/apps store eco system which they pioneered.
There were capable smart phones before but it is said that the iPhone kicked off the smart phone revolution when it launched in 2007. The original iPhone was not sold in Australia however the Australian launch in July 2008 of the iPhone 3G created huge interest. It has been followed by yearly upgrades. Apple have built a strong loyal following for their premium product and the iTunes/apps store eco system which they pioneered.
Yearly updates to iPhone
3GS (2009), 4 (2010), 4S (2011), 5 (2012), 5S/5C (2013), 6/6Plus (2014), 6S/6SPlus (2015), 7/7Plus (2016), 8/8Plus/X (2017), XS/XSMax/XR (2018), 11/11Pro/11Pro Max (2019), 12/12Pro/12 Mini/12 ProMax (2020), 13/13Pro/13 Mini/13 ProMax (2021)
Apple, unlike most other major phone makers, does not manufacture the iPhone themselves. They do the design, component selection and sourcing from a wide range of suppliers. The units are assembled in China by Taiwanese companies Hon Hai (Foxconn) and Pegatron. Between 2007 and 2018 when they stopped reporting iPhone sale numbers Apple had sold 2.2 billion iPhones.
The four models of iPhone 13 were released in Australia in September 2021 and continues the line which has achieved for Apple 17% world and over 50% Australian market share.
The iPhone 13 has a similar feature set to the Samsung Galaxy S22 and most top tier smartphones. The iPhone 13 like all its predecessors has at its heart a proprietary SoC. The iPhone 13′s SoC is termed A15 and it comprises a six ARM core CPU and a four core graphics processor along with a 16 core Neural Engine. The Neural Engine is used to accelerate and optimise machine learning and neural network tasks for speed and energy efficiency. It can be used to accelerate video analysis, voice recognition, and image processing. The iPhone 13 has 4GB of RAM and from 128MB to 1 TB of flash storage.
There is block diagram showing the major components, features and layout of the iPhone 13 Pro Here.
The iPhone System on a Chip A15
The A15 is designed by Apple based on ARM architecture. It is fabricated by Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) using their 5nm chip technology. It contains 15 billion transistors on a silicon dice 110 square mm in area.
Unlike the Samsung S22′s Snapdragon SoC (and most Android phones) the Apple A15 (and all previous iPhone SoCs) do not contain the complex radio baseband logic. In the iPhone 13 this task is performed by a separate Qualcomm X60 modem chip and other chips for WiFi and Bluetooth. The marriage of convenience between Apple and Qualcomm is likely to have to endure until Apple can perfect its own cellular base band when it could presumably incorporate it into the is A series SoC as Qualcomm and others have done for many years.
The specifications for the iPhone 13 are Here. You can see the inside of the the iPhone 13 in the teardown here . There is an iPhone 13 Wiki here.