Archive for March 2017
As requested by a group comprising the major mobile operators and suppliers at MWC in Barcelona the 3GPP has agreed to bring forward the standardisation of the Non-standalone (NSA) 5G NR mode for the enhanced Mobile BroadBand (eMBB) use-case.
3GPP RAN Chairman said “In Non-standalone mode the connection is anchored in LTE while 5G NR carriers are used to boost data-rates and reduce latency. With the updated workplan, NSA will be finalized by March 2018. At the same time, the group re-instated its commitment to complete the Standalone (SA) 5G NR mode by September 2018 and put in place a plan to achieve that.”
The advantage of the change is possible earlier adoption of 5G New Radio NR carriers with their superior speed, latency and capacity. The risk is that the overall 5G standardisation and hence implementation is delayed.
 With everyone who is anyone in the mobile world (108,00 in all) gathered last week at Fira Gran Via in Barcelona there were numbers a plenty on the progress and predictions for the future for the industry.
With everyone who is anyone in the mobile world (108,00 in all) gathered last week at Fira Gran Via in Barcelona there were numbers a plenty on the progress and predictions for the future for the industry.
Some of the big numbers mentioned at WMC by some of the eminent industry people there include:
- At the end of 2016 there were 7.9Bn total mobile subscriptions
- 51% of theses subscriptions are for a smart phones
- These 7.9Bn subscriptions were used by 4.8Bn unique subscribers
- Average subscriber penetration in the developed world is 84%
- In the developed markets penetration in the 16-64 age bracket is 97% i.e. it is saturated
- In the developing markets penetration is 62%
- There is growth in the developing world with 900 million new subscribers expected by 2025
- There are expected to be 5Bn mobile subscribers by the end of 2017
- The industry has spent $1,000Bn on capital from 2010 to 2016
- It is expected that a further $700Bn in capital will be spent from now up to 2020
- $1,230Bn is expected to be spent in capital on 5G by 2026
- There are expected to be 1.1 billion 5G mobiles in service by 2025
- World revenue from mobile service in 2016 was $1,050Bn
- Average data consumed by smartphone users is currently 1.6GB per month
- This will increase to 7GB by 2021
- Video over mobile traffic will increase by 50% each year
- By 2022 video will comprise 75% of traffic on mobile networks
The GSMA run annual World Mobile Congress just completed in Barcelona saw 22 of the largest operators and suppliers calling for a one year acceleration of the standardisation process of NR (New Radio) 5G Radio Access Network RAN. Included in the Group of 22 are Telstra and its mobile network technology supplier Ericsson.
 The current 5G timetable would see networks based on the new RAN NR Release 15 standard deployed from 2020 however many operators and network equipment suppliers are demonstrating 5G like LTE Advance (4.5G) and pre-standard 5G equipment and performance already. These trials and demonstrations and their attendant press releases and market positioning publicity will only accelerate as 2020 approaches.
The current 5G timetable would see networks based on the new RAN NR Release 15 standard deployed from 2020 however many operators and network equipment suppliers are demonstrating 5G like LTE Advance (4.5G) and pre-standard 5G equipment and performance already. These trials and demonstrations and their attendant press releases and market positioning publicity will only accelerate as 2020 approaches.
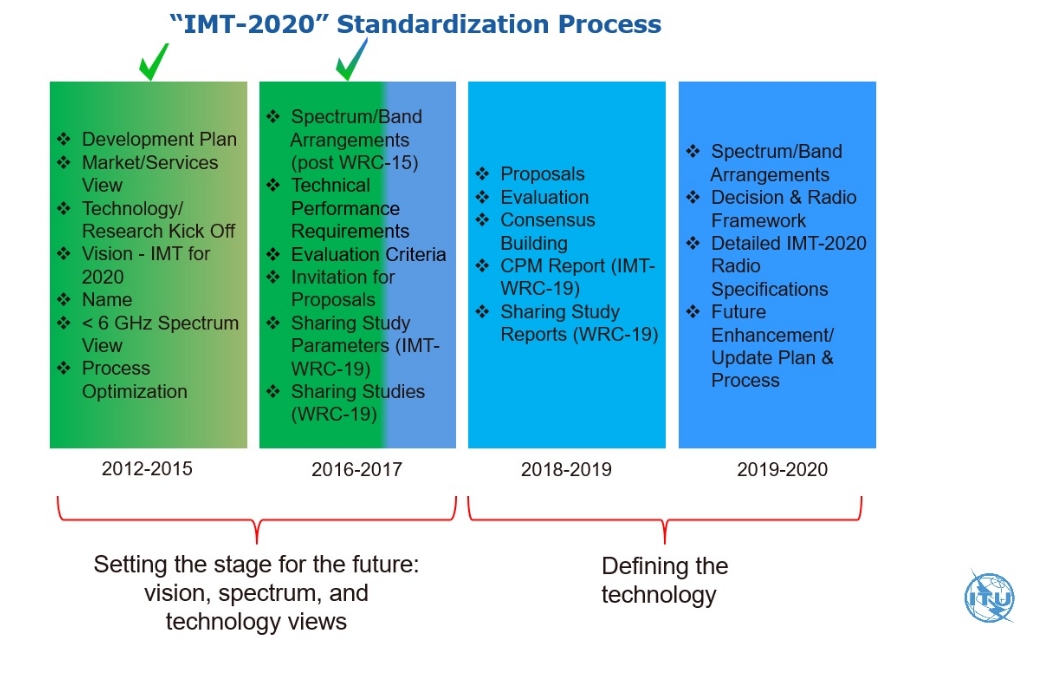
The ITU for its part HERE has set the draft requirements the new technology. The requirements are expected to be finally approved by ITU-R Study Group 5 at its next meeting in November 2017. The requirements for 5G can be summarised as follows:
- Peak data rate: 20 Gbps down / 10 Gbps up
- Peak spectral efficiency: 30 bits/Hz down (8×8 MIMO) / 15 bits/Hz up (4×4 MIMO)
- Area traffic capacity in downlink 10 Mbit/s/m2 for an indoor hotspot for eMBB evolved Mobile Broaband
- User experienced data rate 100 Mbps down / 50 Mbps (5% of the peak data rate)
- Latency: 4 ms for eMBB and 1 ms for URLLC Ultra-Reliable and Low-Latency Communications
- Mobility: Up to 500 km/h with varying requirements for uplink spectral efficiency at different speeds
- Minimum bandwidth: 100 MHz
- Maximum aggregated bandwidth: 1 GHz in bands above the 6 GHz
You can understand that operators would be keen to deploy the more efficient, higher capacity and diverse capability 5G NR equipment as soon as possible to avoid having to spend money on, capable but not as good, 4G LTE equipment much of which will have a reduced service life due to 5G. As well the mobile network equipment providers would like to have the current slow down in their orders for 4G due to impending 5G adoption be as short as possible.
The operator and supplier group is proposing that the Non-Standalone NR be fast tracked by a year allowing them to augment existing LTE RAN and evolved packet core with standards compliant 5G NR in 2019. There is however much work to be done to define the standard summarised in the ITU chart below so it will be interesting to see if the group’s entreaties to speed up the process have any effect.